The Importance of Vitamin D
The Importance of Vitamin D
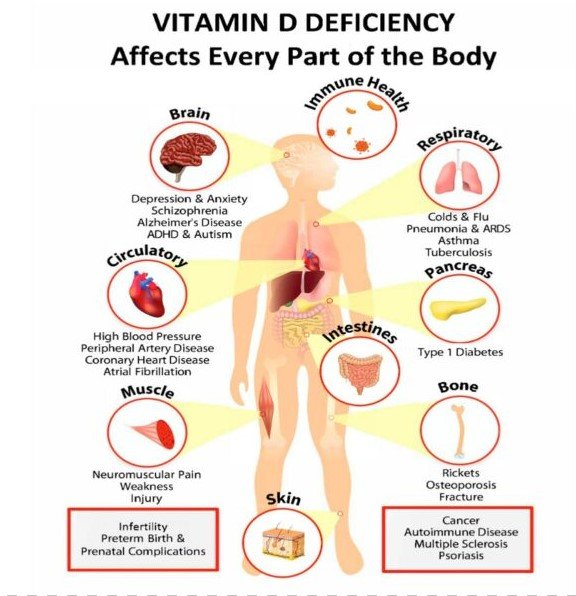
Every cell and tissue in your body has receptors for vitamin D, yet many people are deficient in this vital nutrient. Vitamin D deficiency can negatively impact immune function and lead to inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, autoimmune diseases, depression, sleep issues, digestive problems, bone loss, vascular calcification, and high blood pressure. Low levels of vitamin D are also linked to an increased risk of cancer, heart disease, stroke, multiple sclerosis, and type 2 diabetes.
Causes of Vitamin D Deficiency
In today’s world, several factors contribute to vitamin D deficiency. Air pollution, low-fat diets, stress, smoking, high sugar intake, excessive consumption of processed and fast foods, obesity, and a lack of sunshine all play a role. Additional causes include: Gut inflammation, Absence of the gallbladder, Diabetes, Insulin resistance, Genetic predispositions, Infections, Fatty liver disease, Use of statins (which help lower cholesterol) and etc.
Do We Need Supplements?

Obtaining sufficient vitamin D from diet alone is challenging, making it essential to take proactive measures to prevent deficiency.
Daily Vitamin D Requirements
Vitamin D comes in two forms: ergocalciferol (D2) and cholecalciferol (D3). While D2 requires a prescription, D3 is available over the counter and is generally easier for the body to absorb.
Doctors assess vitamin D levels by measuring 25(OH)D in the blood, the storage form of vitamin D in the body. There is no universally agreed-upon definition of optimal blood levels, but the National Institutes of Health (NIH) recommends the following:

The amount of vitamin D needed to treat a deficiency depends on the severity of the deficiency and individual risk factors. A doctor may initially prescribe a higher dose of 6,000 IU of D3 daily. Once levels exceed 30 nanograms per milliliter (nmol/L), a maintenance dose of 1,000-2,000 IU daily is usually recommended.
Suppose you are at high risk for deficiency due to certain medications, dark skin, obesity, or conditions that inhibit nutrient absorption. In that case, your doctor may start you on 10,000 IU of D3 daily until your blood level exceeds 30 nanograms per milliliter. After that, a dose of 3,000-6,000 IU of D3 per day may be suggested.
It’s advisable not to purchase supplements without a blood test. You can take charge of your health by requesting a 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) blood test, the most accurate and commonly used method to assess vitamin D levels.
For those looking to strengthen bones, taking vitamin K2 alongside vitamin D3 is beneficial. Vitamin K2 plays a critical role in the transportation of calcium, while vitamin D enhances the absorption of calcium from the gut into the bloodstream. K2 helps keep calcium out of soft tissues and strengthens bones.
In my next article, I will discuss how D3 and K2 work together to address issues like high blood pressure and weak bones.
*Disclaimer: This article is intended for general informational purposes only. It should not be used as a self-diagnosis tool, and it does not replace medical examination, diagnosis, treatment, prescription, or professional recommendations. Always consult with a healthcare professional before trying any new remedies or treatments.





I am extremely inspired along with your writing skills and also with the format on your blog. Is that this a paid topic or did you customize it yourself? Anyway keep up the excellent high quality writing, it is uncommon to see a nice blog like this one nowadays!